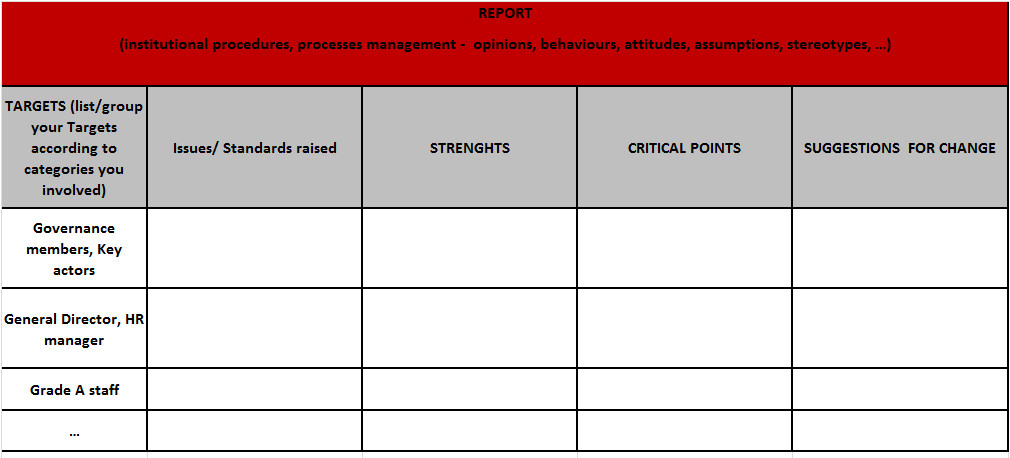
2.1. Students
Recommendations of information to be included in this section:
Describe the situation of undergraduate, master, PhD students regarding number of students in AY 2015/16.
- Name the programs with a balanced (60/40) amount of male/female students.
- Name those programs where the number of male students is over 60%
- Name those programs where the number of female students is over 60%
- Analyse of any conclusions regarding areas of study can be done.
Regarding part-time/full-time study and degree duration look at the percentages of male and female students in each case; look at any major differences that might arise.
In the cases (Some RPOs don´t have this data) where information about the application for AY 2015/16, calculate the acceptance rate and if differences between amount of male and female student numbers happened. Describe it.
Same with the graduation rate. Are there any programs/masters/PhD areas where the graduation rate of male or female students was relevantly higher or lower?
2.2.- Selection and recruitment
Recommendations of information to be included in this section:
Firstly describe the selection and recruitment processes in a general way, analysing the process of selecting the new people hired in the institution in the last year and the inclusiveness of them, and then more specifically to the processes where the last 3 women and the last 3 men were hired in the institution, it will explore those in detail. The composition of the selection committees, were they apply, will also be taken into account for this analysis.
For our conclusions in this section pay attention at things such as:
Regarding the outcome of the process
- Looking at the percentages of Women CVs and Men CVs received, is there a balance? Do more women/men apply in general? Does this change for specific positions/departments? Do the numbers show any tendencies in this respect/anything we should pay attention to?
- Are the percentages of women and men CVs received and the percentages of finalist and hired people linked? Is there any “positive action” taken to make sure that the gender with lowest representation is also present (if such a case)? If people at any cases are hired by direct appointment also specify.
- If we have relevant information about support programmes/activities happening in the RPO please specify – those would be linked to the “positive actions” mentioned at the previous point.
Regarding the design of the processes themselves
- Where there any processes where they specifically looked for women candidatures? Is there any really masculinized area in the RPO where such a policy could be needed?
- The type of advertisement used. If only the two first items have been answered yes, then we can conclude that inclusive language has been used during the process. If not, we would there identify an issue where attention should be paid in future. A critical issue to pay attention to. In the cases where a mix of the two happened, it will be interesting to compare the outcomes of both kinds of advertisements: did more men/women reply in any of the cases? In which? Is there an standard set of questions to be used in the interviews? (this might have arisen in the qualitative)
- The way of approach. Look if there are any relevant tendencies/differences among men and women in this sense and describe the way it has happened in the RPO.
- Selection committee. Look at the composition of the Selection Committee, are there balanced numbers in terms of positions in the hierarchy of the RPO and men and women? Look at the horizontal and vertical segregations[1]and describe the composition of the Committee in terms of vertical/horizontal segregations.
2.3.- Career progression
Recommendations of information to be included in this section:
A description of the graph 2.3.1 will be made with special attention paid to things such as:
- Percentages of M and W by level at the moment they were hired. Where there differences in terms of balance? Level?
- In the graph, can we see any differences in the careers of those men/women? Is the line more horizontal in any of the cases (showing lack of progress in terms of level)?
- How many people left from those who started? This might be caused by different reasons and relevant information might have arisen in the qualitative. If so make a link with that information. If not, describe the situation in terms of percentage of men who left and percentage of women. Compare them and if there are relevant differences then it might be a critical issue, at least an issue to look at deeper in the future.
The information gathered in chart 2.3.2 will be made by specifying:
- Average age of women in high level and average age of men in high level positions. Is there a difference?
- Average age of women in medium level and average age of men in medium level positions. Is there a difference?
- Average age of women in low level and average age of men in low level positions. Is there a difference?
- When applicable also look at the technical and administrative staff data.
- General conclusions regarding age and gender by level. In the cases where certain tendencies have appeared. For example if women are only relevantly present in some categories, in terms of numbers.
Description of career promotions within the institution with the information gathered in Chart 2.3.3.
- Are there differences in % of men and women who asked for promotion in reference to the ones who met the criteria?
- In the number of men and women who progressed in the promotion process?
- In the amount of years who stayed in their previous categories? Do men/women stay longer in a category or not?
- Description of selection committee and the gender of the Chair of the committee.
Finally, if there is relevant information regarding support and training programmes will describe it here.
2.4.-Gender pay gap
Recommendations of information to be included in this section:
- Describe the average salary of women in Grade A and compare it to the one of men. If there are differences state the ones caused by amount of years in the institution or other causes.
- Describe the average salary of women in Grade B and compare it to the one of men. If there are differences state the ones caused by amount of years in the institution or other causes.
Describe the average salary of women in Grade C and compare it to the one of men. If there are differences state the ones caused by amount of years in the institution or other causes.
[1] Horizontal segregation is understood as under (over) representation of a certain group in occupations or sectors not ordered by any criterion (Bettio and Verashchagina, 2009). Horizontal segregation refers to the concentration of women and men in professions or sectors of economic activity. Horizontal segregation is a constant in the labour market in all OECD countries (Rubery and Fagan, 1993; Anker, 1998; OECD, 1998).
– Vertical segregation referred to the under (over) representation of a clearly identifiable group of workers in occupations or sectors at the top of an ordering based on ‘desirable’ attributes – income, prestige, job stability etc, independently of the sector of activity. Under-representation at the top of occupation-specific ladders was subsumed under the heading of ‘vertical segregation’, whereas it is now more commonly termed ‘hierarchical segregation’” (Bettio and Verashchagina, 2009, p. 32)